Black leg
It is serious cabbage disease caused by the fungus Leptosphaeria maculans (Phoma lingam). Symptoms of black leg usually appear as oval, sunken, light brown cankers, often with a black or purple margin, near the base of the stem. The canker enlarges until the stem is girdled and the plant wilts and dies. Severely infected plants are stunted. Infected plants eventually wilt and then turn dull blue-red. With black leg, plants may suddenly collapse due to stem deterioration.
Host range: It includes most of crucifers, but with varying degrees of susceptibility. Most susceptible: cabbages, Swedes, kohlrabi and white mustard. Medium susceptible: cauliflower, turnip, broccoli, rape, kale and collards. Resistant: horseradish, winter-cress, shepherd's purse and pepper grass.
Symptoms: All above parts of a plant may be affected from seedbed to harvest.
Seedlings: Cotyledon infection causes seedlings to die early. This is often overlooked in the seedbed. Stems: An elongated, light brown, sunken spot or lesion with purplish margin forms on stems near the soil line. Lesions gradually extend upward and downward and eventually girdle the stem and the stem turns black. Small, black dots (fruiting bodies of the fungus: pycnidia) appear on the affected area. Internally, the affected stem shows a brown, dry rot. Affected plants often wilt suddenly and die or topple over later as the heads in case of cabbages enlarge.
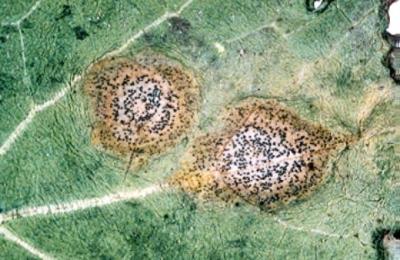
Leaves: Inconspicuous, circular, light brown to grayish spots form on leaves. The spots soon become well defined and develop ash-gray centres in which large number of minute black bodies (pycnidia) are scattered. The presence of pycnidia on cotyledons, leaves and stems distiguishes blackleg from other crucifer diseases.
- Avoid wet soil. Blackleg is most destructive in wet soil.
- Diseased leaves should not be fed to farm animals if manure is to be used on crucifer fields
- Plant tolerant/resistant varieties where available. Check with seed dealers
- Plough in diseased crop immediately after harvest
- Practise a 4-year rotation since the fungus remains alive in soil for at least 3 years
- Properly weed production fields
- Use certified disease-free seed since blackleg is seedborne (i.e. carried on and in the seed). In case of using own seed, treat the seed in hot water and then dress with a recommended fungicide (e.g. Captan; Thiram; etc)
- Seedbeds and should be established in soil that has never been planted to crucifers
- Hot water treatment of own seed to prevent seed borne diseases such as black leg is recommended where the disease has appeared before. For more information on Hot water treatment click here.
