Scientific name
Cordia sinensis
Order / Family
Boraginaceae
Local Names
Boran (Mader, Harores); Chonyi (Mkayukayu); Gabra (Madeer); Giriama (Mderia); Kamba (Muthei munini); Kipsigis (Nokirwet); Maasai (Oldorko); Malakote (Mutalya chana); Marakwet (Adomoyon); Orma (Mader); Pokomo (Muhale); Pokot (Adomeyon) Rendile (Gayer); Samburu (Llgoita) Swahili (mnya mate,mkamasi); Tugen (Adomeyo)
Introduction
Distribution:
It is native to Egypt, Ethiopia, India, Israel, Jordan, Kenya, Madagascar, Mozambique, Namibia, Pakistan, Senegal, Somalia, South Africa, Sri Lanka, Sudan, Tanzania, Yemen and Republic of Zimbabwe. In Kenya, it is widespread in the drier parts of the country but absent in Western and Nyanza provinces.
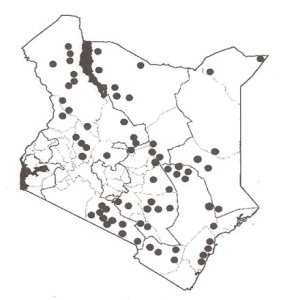 |
| Distribution of Cordia sinensis in Kenya |
| © Maundu P. and Bo Tengnas. (2005). Useful trees and shrubs for Kenya, World Agroforestry Centre. |
General Information about the Tree:
Flowering occurs in December to February and August while fruiting happens from April to June, and in December, fruits are eaten by monkeys, baboons and birds which are the main dispersal agents. It is a very important tree in dry areas. Its branches are flexible, light and they do not snap; are used for supports of camel pack-saddles. Ripe fruits are eaten raw; the sweet mucilaginous pulp may be eaten, while the fruit cover and seeds are discarded.
Biophysical Limits:
This species is common in dry riverine vegetation, usually with Salvadora persica, or in open bushland in low altitude arid and semi-arid areas on termite mounds and in littoral scrub. Altitude ranges between 0 and 1500 m. Mean Annual Rainfall is between 600 - 1000 mm annually and it prefers alluvial, sandy, red loam and rocky soils in moist river beds.
Propagation and Tree Management
Cordia sinensis is fairly fast growing and tolerates lopping, pollarding, and coppicing. It can be propagated by seedlings and wildings. Several seedlings may germinate from each stone. Can be pricked out
Products:
- Medicine: The roots and bark are used for stomach disorders in both children and adults. A decoction of boiled roots is used to treat malaria but can cause an abortion. Bark and roots are mixed to treat conjunctivitis in cattle.
- Fodder: A very important source of fodder for goats, sheep, cattle and camels in dry areas.
- Food: The sweet and sticky tasty pulp of the fruit is eaten fresh and often put in porridge as a sugar substitute. The fruit pulp is sometimes used to make juice or brew local beer and sometimes mixed with tamarind (Tamarindus indica) juice and fermented.
- Gum: The clear gum from the tree is edible.
- Timber: The wood is used in the construction, furniture and for agricultural implements (such as tool handles, walking sticks, clubs, wooden spoons, stirrers and stools).
Services:
- Shade in the hot sun.
- Soil protection from erosion.
Pests and Diseases
There is no information about the diseases and pests that affect Cordia sinensis.
Information Source Links
- Beentje HJ. (1994). Kenya trees, shrubs and lianas. National Museums of Kenya.
- Maundu PM et al. (1999). Traditional food plants of Kenya. National Museums of Kenya.
