Foot Rot in Sheep/Goats
|
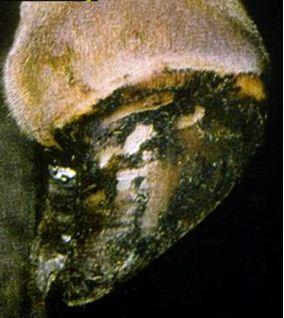
In sheep/goats Foot Rot is a serious herd problem that can affect many sheep/goats and spread rapidly through the entire flock. In most cases more than one foot is affected. Causes In Foot Rot two organisms are required to start the infection - Fusobacterium necrophorum and Dichelobacter nodosus. Fusobacterium lives in the sheep's guts and environment and can also affect cattle. Fusobacterium alone cannot cause Foot Rot. Dichelobacter lives only in the affected hooves of carrier sheep/goats and is the main cause for foot rot. During rainy Dichelobacter can survive for maximum two weeks on soil or pasture and infect more sheep/goats. Foot Rot is transmitted via the contaminated environment. If healthy sheep/goats share pasture, watering points and/or the boma with Foot Rot infected sheep/goats they pick up the infection while passing through contaminated areas
Signs
|
|
Prevention & Control
|
|
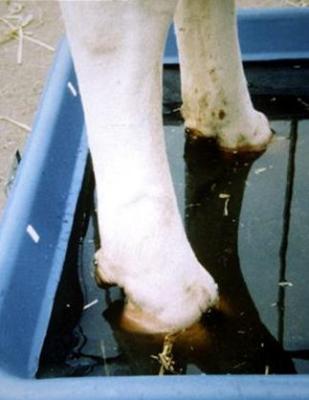
Treatment
The success of any treatment is much greater if the sheep are kept in a completely dry environment after treatment. The feet of treated sheep should be examined every 1-2 weeks to identify those needing further treatment.
Diseases with similar signs/symptoms
|
|