|
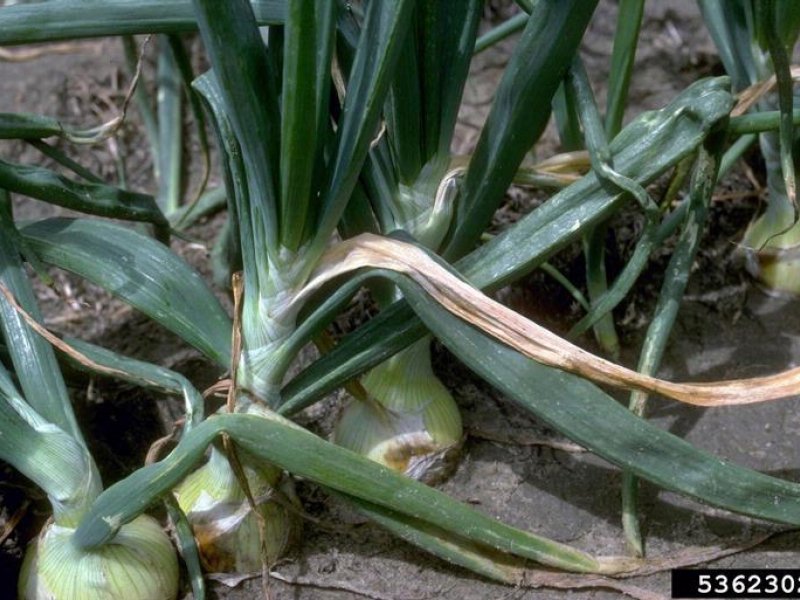
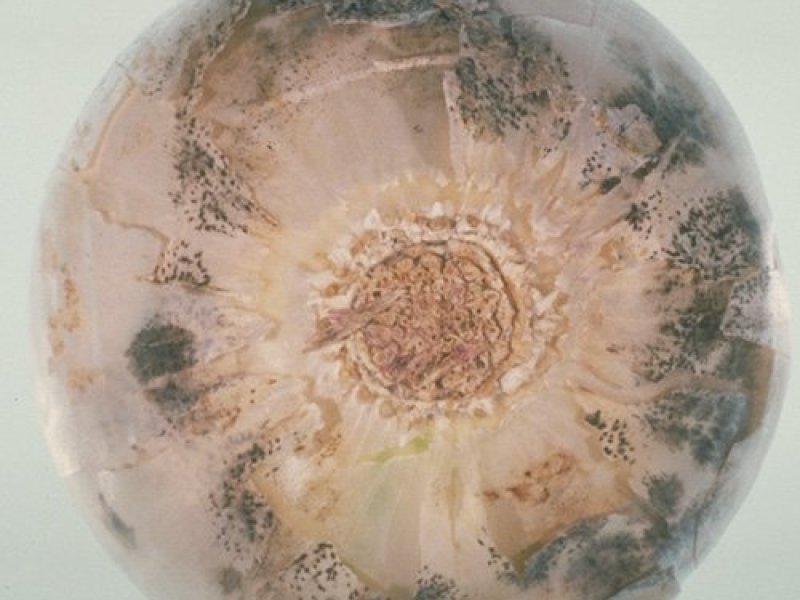
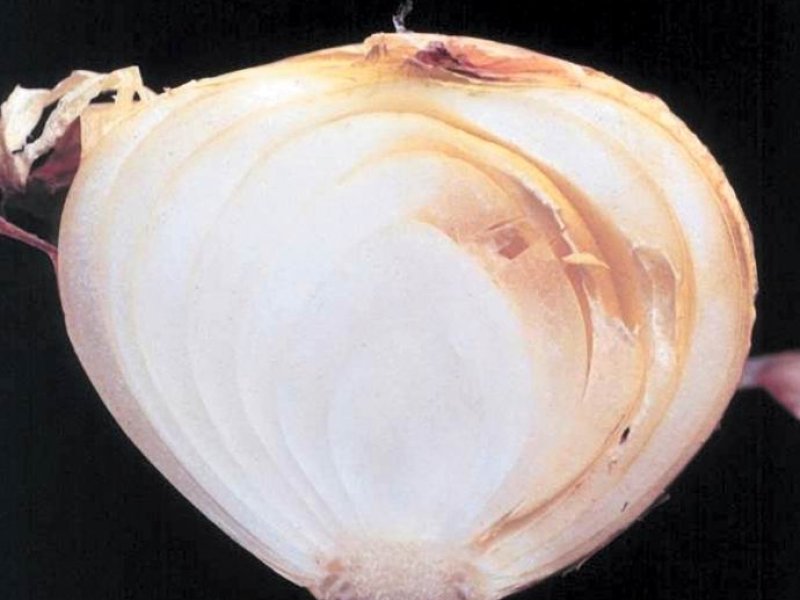
Anthracnose (Onion smudge) (Colletotrichum circinans) It usually appears in fields just before harvest and continues to develop during storage period. Under warm and wet soil conditions, it can cause seedling damping-off. The most common symptom is the small dark green or black stains (dots) on outer scales of bulbs. The dots develop concentric rings. In severe cases, the fungus attacks the living tissue causing a collapse of fleshy scales. On coloured onions, the fungus is restricted to the neck of the bulbs making the flattened leaves colourless. The fungus survives on onions, sets and in the soil. Warm moist conditions favour development of the disease. Optimum temperature for infection is from 23.9 to 29.4 °C. White onions are very susceptible to the disease. Reduced market value results from marred bulb appearance and bulb shrinkage. It also attacks leeks and shallots.
|
|
|
What to do:
|
|
Bacterial soft rots (Erwinia carotovora subsp. carotovora) This is a big cause of loss in storage onions. Bacteria Erwinia carotovora subsp. carotovora) can enter the neck tissue as plants mature and then invade one or more scales. At this stage, the affected tissues are water-soaked and pale yellow to light brown. As the rot progresses, the invaded fleshy scales become soft. Diseased bulbs can be diagnosed by pressing on the bulb: a watery, foul-smelling fluid often can be squeezed from the neck of diseased bulbs. Bacterial soft rot bacteria enter only through wounds. Onion maggots (Delia antiqua) may carry the bacteria and introduce them while feeding. Onions with mechanical injuries, bruises or sunscald under warm, humid conditions are particularly susceptible to bacterial soft rot. Soft rot can affect many vegetables including carrots, celery, potato and parsnip.
|
|
|
What to do:
|
|
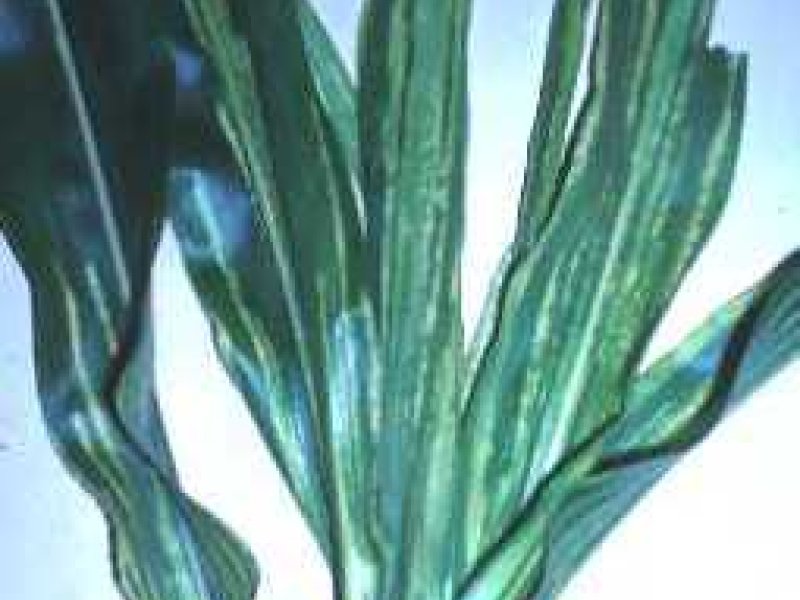
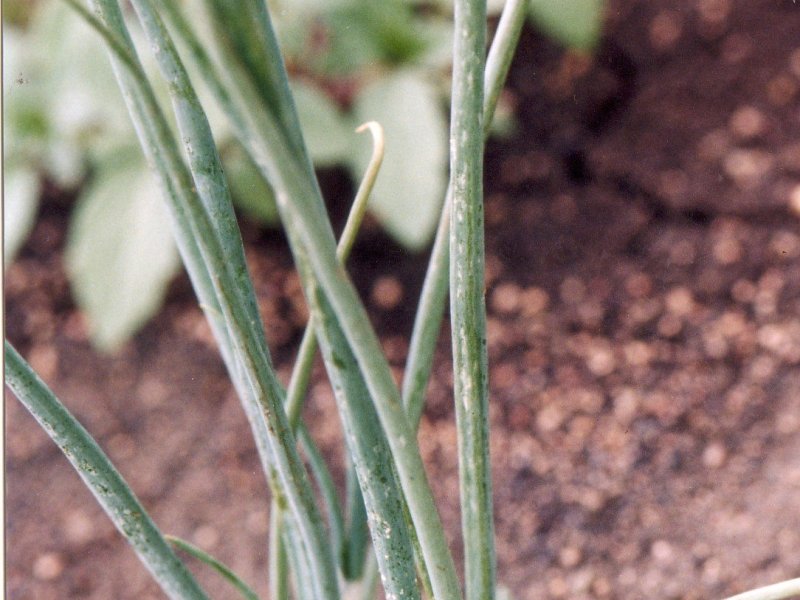
Downy mildew (Peronospora destructor) It attacks young plants, appearing as white specks, usually confined to the oldest leaves of young plants. A greyish white mould develops rapidly in cool damp weather and progresses down the sheath, and plants eventually fall over and dry up. Optimum temperatures for fungal growth are between 13 and 20 °C. Because of the temperature requirements of the fungus, the disease is more serious in higher cooler areas. The fungus survives in seeds, bulbs, sets, and on plant debris. Spores are carried long distances by air currents. The fungus can infect onion, Welsh onion, Egyptian onion, garlic, shallot, leek and possibly some other species of Allium.
|
|
|
What to do:
|
|
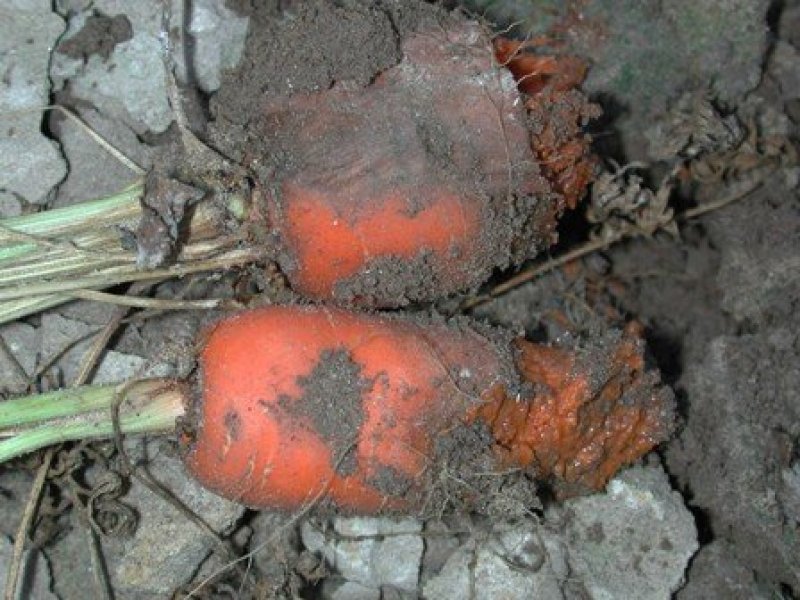
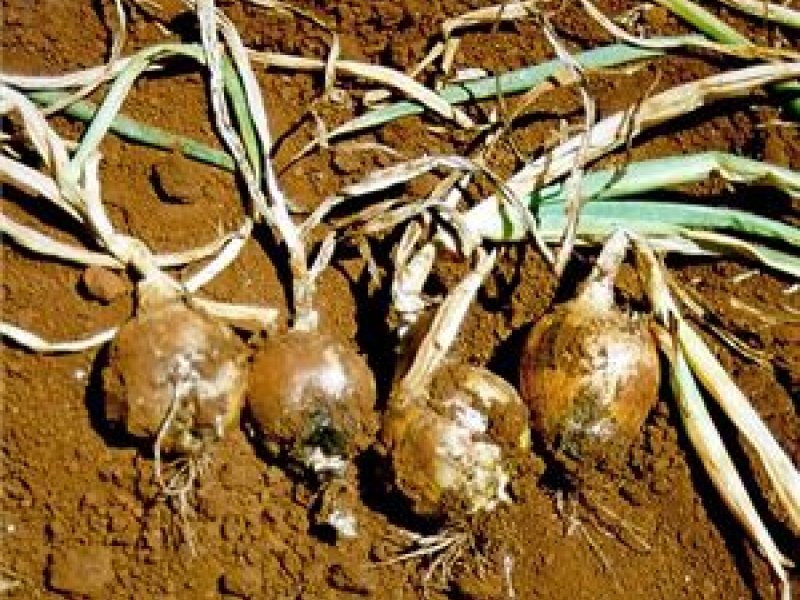
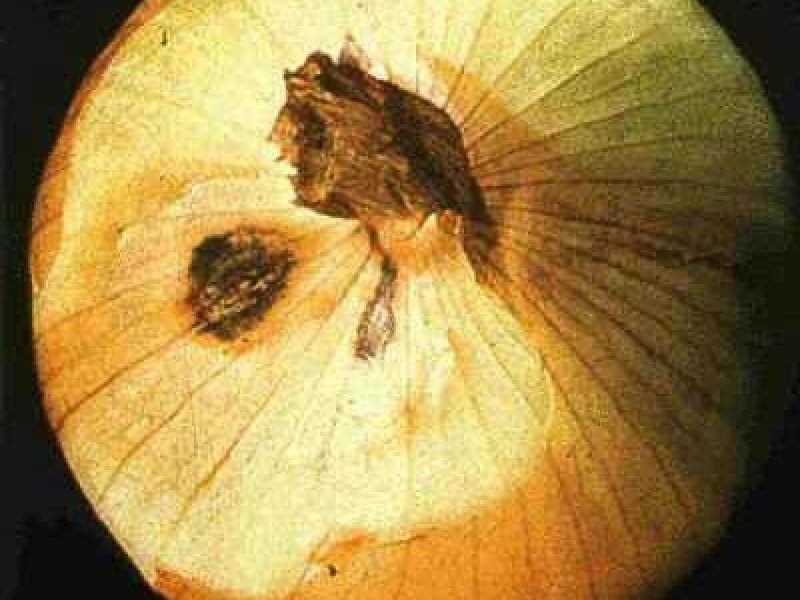
Fusarium basal rot (Fusarium oxysporium f.sp. cepae) The above ground symptoms constitute yellowing of leaf blades at the tip. The yellowing at later stages covers the whole blade. The affected leaves shrivel and decay. Diseased plants can be easily pulled out because the root system is rotted. Affected roots are dark brown, flattened, hollow and transparent. When diseased bulbs are cut vertically, a brown discolouration is evident. The fungus survives in any soil moisture that permits crop growth. Infection is facilitated by injuries to root system, Losses can occur in the field and in storage. The disease is most prevalent where onions are grown under high temperature conditions. Although of no economic importance the disease could attack garlic, shallots, chives and leeks. It also can survive in weed, Oxalis corniculata.
|
|
|
What to do:
|
|
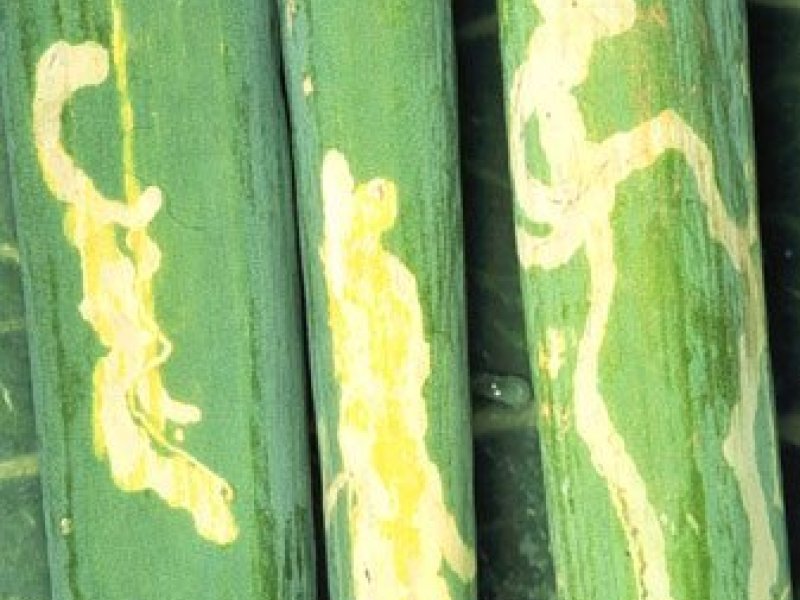
Leafminers (Liriomyza spp.) Leafminers may cause damage to green onions. Damage is largely cosmetic, and mining on leaves may cause rejection of marketed onions, but generally does not affect plant growth. Damage in dry onions and garlic is of little concern unless populations become high to prematurely kill foliage. |
|
|
What to do:
|
|
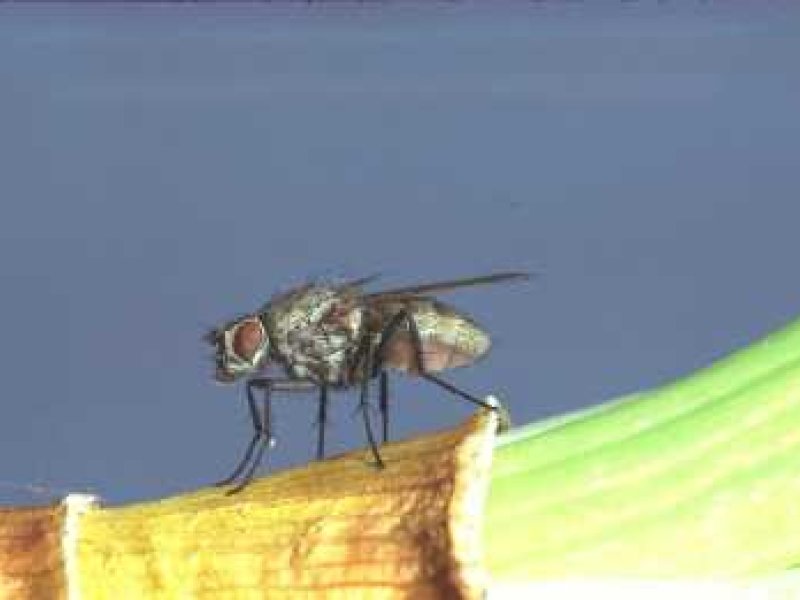
Onion fly (Delia antiqua) The larvae of the onion fly, also called onion maggot is a major pest of onions. The maggot is small (about 8 mm in size when fully grown), white-cream coloured. It eats the lateral roots, then tunnels into the taproot and sometimes bores into the base of the stem. Attacked leaves wilt and the leaves turn bluish. The plants become shrivelled or eventually die. The maggots feed just above the base of seedlings killing them. A maggot can attack several seedlings in succession. This causes poor plant establishment resulting in many gaps in the field. The maggots are also found inside developing onion bulbs. Their feeding exposes the plant to infection by diseases such as bacterial soft rot. Pupae are light to dark-brown in colour, and about 7 mm in length. Pupae are found in the soil near the base of the plant. The adult is a brownish grey fly, somewhat smaller than house flies. When at rest, they keep their wings folded one over the other. Adult flies do not cause damage. They lay eggs in the soil surface near the germinating plants. Onion maggots are adapted to cool, wet weather, so usually they are less of a problem during hot dry periods. They prefer soils heavy in organic matter. The onion maggot attacks plants related to onion such as leeks, shallots and garlic.
|
|
|
What to do:
|
|
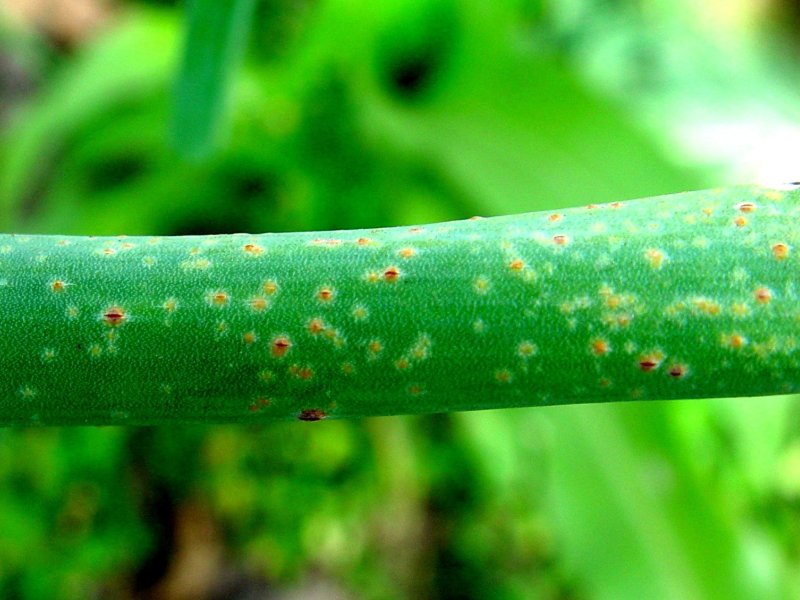
Onion rust (Puccinia porri) Affected leaves show small reddish to dusty orange spots (pustules). These later turn black and are covered until maturity by leaf epidermis. Leaves that are heavily infected turn yellow and die prematurely. A new crop of leaves may develop and the bulb size is usually reduced. The fungus attacks also leek, shallot and some wild species of Allium. The disease is favoured by high humidity coupled with moderate to low temperatures. Also excessive nitrogen in the soil favours disease development.
|
|
|
What to do:
|
|
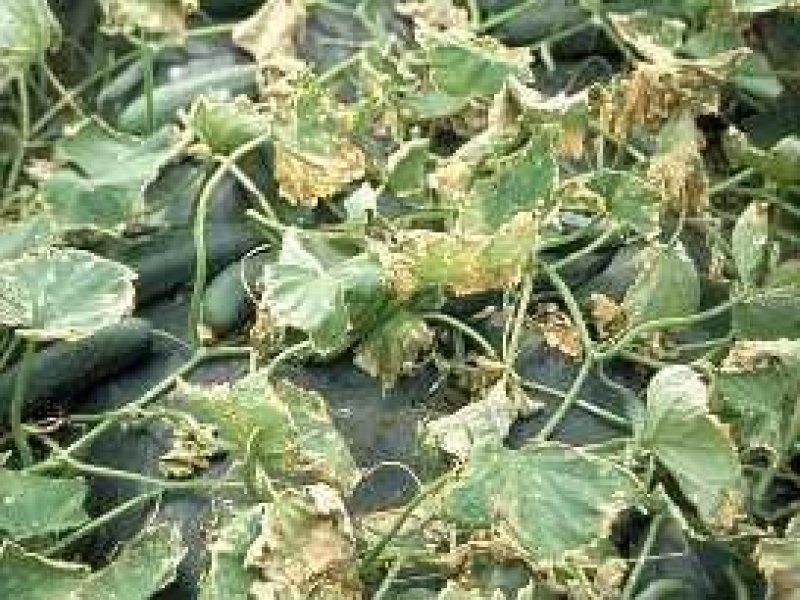
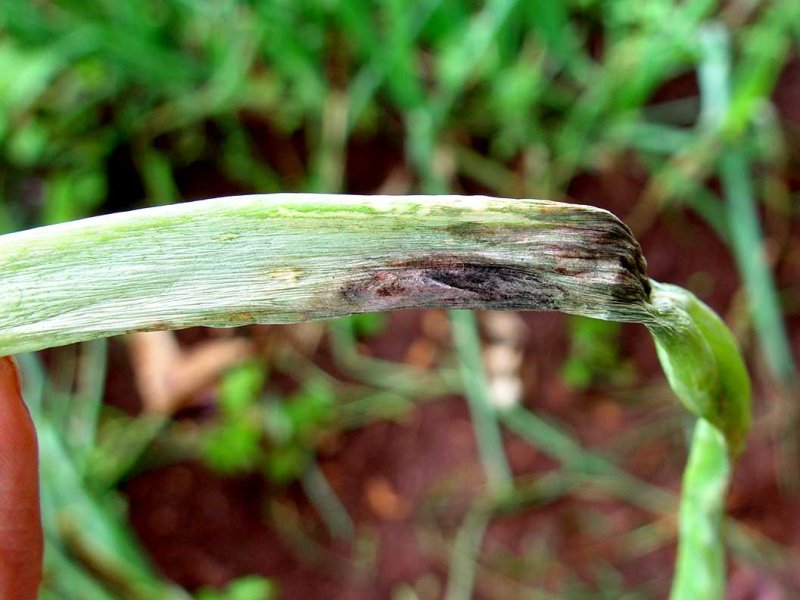
Purple blotch (Alternaria porri) Purple blotch attacks onion, garlic, leek and other Allium crops. Initially, small white sunken spots develop on the leaves. These enlarge and under moist conditions, turn purple with a yellowish border and are often covered with a sooty deposit of spores. After 3-4 weeks the leaves turn yellow and collapse. Bulbs may also be attacked, mainly at the neck. This can be seen as a yellow to reddish watery rot. A good timing of sowing or transplanting can minimise purple blotch attack by A. porri, depending on the local environmental conditions. The fungus requires rain or persistent dew for reproduction. It can grow through a wide temperature range of 6 to 33.8 °C. Optimum temperature of fungal growth is 25 °C.
|
|
|
What to do:
|
|
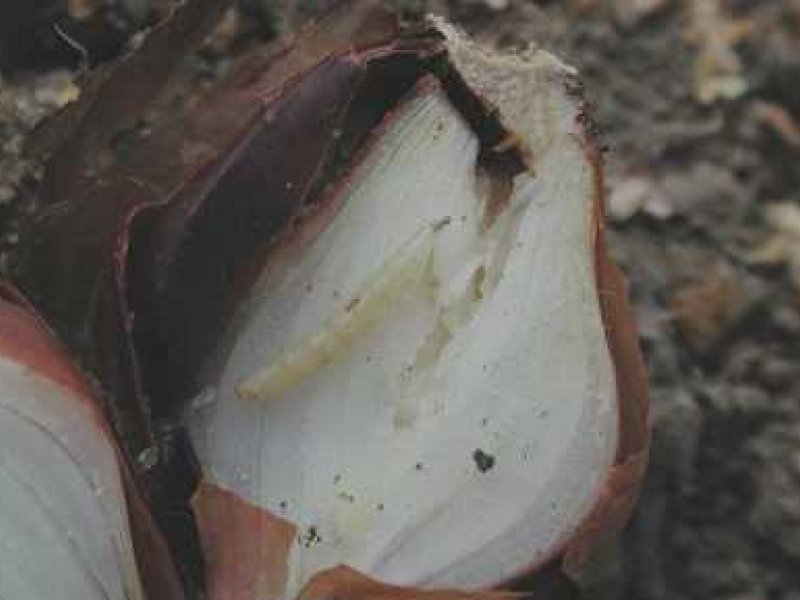
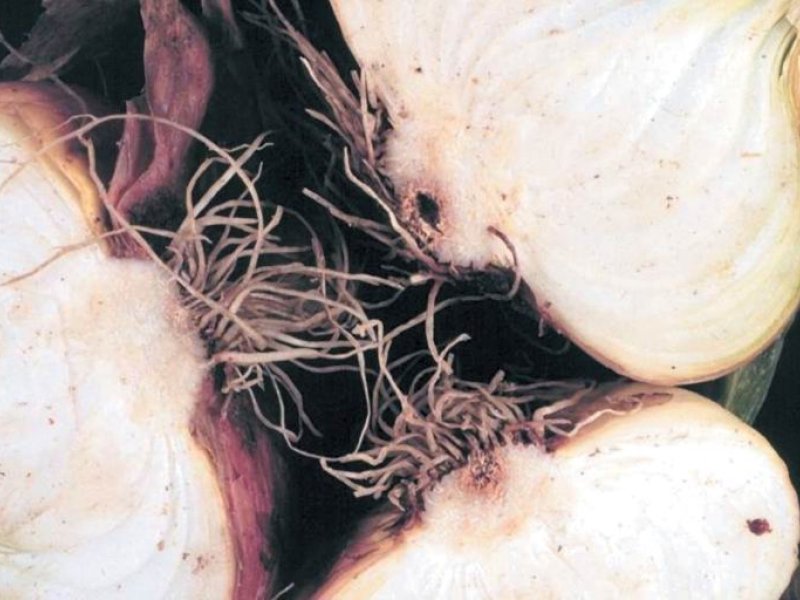
Slippery skin (Pseudomonas allicolai pv. allicola) There are no symptoms on the outer surface of bulbs during early stages of disease development. When the bulb is cut open lengthwise, one or more of the inner scales can be found water-soaked or appears as if it has been cooked. The rot does not progress crosswise in the bulb. After the decay has progressed, the tissue begins to dry, the onion shrivels and secondary organisms can enter and cause a wet rot. The base of the bulb can be pressed hard enough to cause the centre core to slip out at the top, and for this reason the disease is known as slippery skin. The disease is favoured by high moisture.
|
|
|
What to do:
|
|
Sour skin (Pseudomonas cepacia) In contrast to soft rot and slippery skin, infected scales are not water-soaked but are slimy and yellow. Symptoms usually visible only after onions are dug. The upper portion of the bulb shrinks, and in advanced stages of the disease, the outer dry skin readily slips off during handling while the centre of the bulb still remains firm. Outer layer of scales often becomes darkened and almost orange. Decay of inner scales leads to a soft rot that has a sour, vinegar-like odour. The disease is favoured by wet warm conditions.
|
|
|
What to do:
|
|
Onion thrips (Thrips tabaci) The onion thrips are major pests of onions throughout Africa. The onion thrips attack an extensive range of crops, including cereals and broadleaved crops. They are tiny (1 mm in length), slender and very mobile insects. Adult thrips are pale yellow to brown in colour. Immature thrips are whitish to pale yellow. Both immature and adult thrips pierce the upper surface of the leaves and feed on the plant sap, generally on the developing leaves, deep inside the plant. This results in white and silvery patches on the leaves. The excreta of the thrips are clearly visible as small black dots on the silvery leaves. Severe infestations can cause browning of the leaf tips, slowing of plant growth, distortion of leaves and bulbs, and reduction in bulb size. Although thrips feeding during the early bulbing stage is the most damaging to yields, thrips must be controlled before onions reach this stage so that populations do not exceed levels that can be adequately controlled. Onions can tolerate higher thrips populations closer to harvest.
|
|
|
What to do:
For more information on neem click here.
For information on garlic bulb extract clik here
|
|
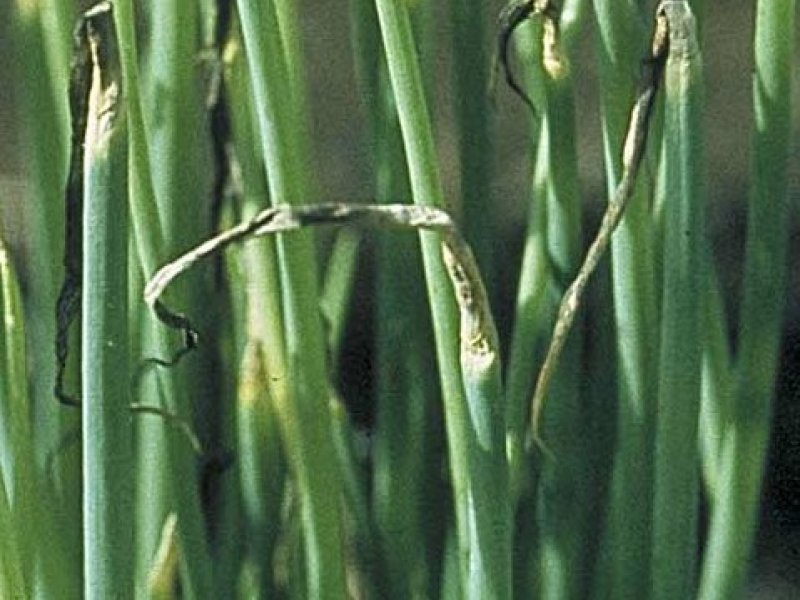
White bulb rot (Sclerotium cepivorum) The disease occurs mainly in the field and seldom causes injury in storage. The disease is called white rot because of characteristic basal bulb rot where the tissue is covered with white mat of fungal growth. Later numerous rounded black fungal bodies (sclerotia), each about the size of a pin's head, develop. The leaves of diseased plants decay at the base, turn yellow, wilt, fall over and die. The older leaves are the first to die. The roots of affected plants are usually rotted making the plants easy to pull. Optimum temperature range for infection is from 15 to 18.3° C. The fungus survives in the soil as sclerotia and also in diseased onion sets and wild onion. It is most severe in light cool moist soils. Its host range includes Welsh onion, garlic, leek, shallot and some species of wild onion.
|
|
|
What to do:
|
Geographical Distribution in Africa
Geographical Distribution of Onion in Africa. Updated on 8 July 2019. Source FAOSTAT.
© OpenStreetMap contributors, © OpenMapTiles, GBIF. https://www.gbif.org/species/2857697
Read more
Local Names (Detailed):
Algeria: Elbesla (Popular name); Âzalim, Âzlim (Berber), Oignon (Local French), (African Museums).
Angola: (oka) sapola (Umunundu); (O)Vayu (Umubumbu), Cebola (Portuguese)
Benin: Wanakou (Bariba); Aloumassa, Ayomassa Vovo, Massa (Fon, Goun); Ayoman Wéwé (Watchi); Ambassa (Yoruba); Agnoman (Fon)
Burundi: Igitunguru (Kirundi)
Burkina Faso: Sasinsala
Cameroon: Tingnere (Fulfuldé); Oignon (local French); Lilang (Brassa); Ayang (Ewondo), Oignon (French); Anoussi (Ghomala’a)
DRC Congo: Matungulu (Swahili), Igitunguru (Kinyarwanda), Ronye (Hunde), Itunguru (Mashi), Matungulu (Nyanga); Bola, Nyasa (Kikongo); Itunguru (Shi) Honyo-itunguru (African Museums)
Ethiopia: Shinkurt (Amharic); Shunkkurttiya (Konta); Keyh-shgurti (Tigrigna) (African Museums)
Ghana: Gyene (African Museums)
Madagascar: Tongolovazaha; Dongolo (Antakarana); Mangafaka, Tongolombazaha (Malgache); Oignon (French); Onion ( Anglais) (African Museums)
Mali: Diaba (Bambara); Toume (African Museums)
Mauritius: Zoiyuon (Mauritian Creol and Bhojpuri); Zoignon (Rodrigues Creole), (African Museums)
Morocco: Bassla (Arabic), Oignon (French); Azalim (Tamazighet)El-besla (African Museums).
Nigeria: Ayim (Ibibio); Alubosa (Yoruba); Yabasi (Igbo); Alabasa (Hausa); Alubarha (Bini), Yabasa (Ibo); Alubosa Yoruba); Alubarha (Binis); Uta (Efik) (African Museums).
Kenya: Kitunguu, (Swahili), Gitunguru (Kikuyu); Kitunguu (Maasai); Kitungu (Kamba); Gitunguru (Meru)
Rwanda: Igitunguru, Gitukura (Kinyarwanda) (African Museums).
Sierra Leone: Yabas (Krio); Yawe (Mende); Ta Yabas (Temne) (African Museums).
South Africa: Itswele (isi Xhosa); Eive (Basotho); Ui (Africaans) (African Museums).
Togo: Sabulè (African Museums).
Uganda: Katunguru (Runyankole, Runyaruguru); Katungulu (Lusoga); Ekitunguru (Ngakarimojong) (African Museums).
General Information and Agronomic Aspects
Introduction
Onion is a biennial vegetable grown in temperate zones as an annual. Onion (Allium cepa) is classified within the family Amaryllidaceae and the genus Allium. The genus is one of about fifty-seven genera of flowering plants under the family with more than 500 species. Other significant species within the genus Allium include: Garlic (A. sativum), Green onion or scallion (Allium fistulosum), Leek (A. porrum), and Chives (A. schoenoprasum).
Ⓒ Adeka et al., 2005
Allium cepa is believed to have originated in Central Asia (between Turkmenistan and Afghanistan). This region is notable as it is home to some of its wild relatives to this day. Its cultivation has traversed the globe, adapting to varied climates and soils. Flourishing as a cool-season crop, it predominantly thrives in temperate regions.
© Maundu, 2005
Onions boast diverse and widespread utilization across various domains: In general, onions are used for salads (bunching onion or sliced full-grown bulbs for use as topping for sandwiches, burgers, and hotdogs etc ), pickling (e.g. silver skin onions), cooking (add flavor, aroma, and texture to a wide array of dishes, including soups, stews, salads, curries etc.). Onions have been historically recognized for their potential health benefits. They contain bioactive compounds like quercetin, which possess antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. These properties may contribute to their use in traditional medicine (e.g. as a diuretic, alleviating coughs, treating colds and infections, and making poultices for wounds and insect bites). The pungent smell of onions has been used to deter insects and pests in gardens and households.
(Messiaen & Rouamba., 2004,PROSEA, 2016,Plantvillage, (n.d)
In the tropics the varieties that do well are in effect annuals as they can produce seed within the first year of growing. Nutrient-wise 100 g of onion provides about 30 g calcium, 0.5 mg of iron, vitamin B, 0.2 mg of riboflavin, 0.3 mg nicotinamide, and 10 mg ascorbic acid (vitamin C).
In general, onions are used for salads (bunching onion or sliced full-grown bulbs), pickling (e.g. silver skin onions), cooking (such as in soups) and frying (for example, with meat). Onions are particularly suited to smallholder farming in most countries. It also plays an important role in traditional medicine (e.g. as a diuretic). In the tropics onions can be grown year round where irrigation is possible.
Species account
A. cepa is a biennial plant grown in temperate zones as an annual (harvested after one growing season). The plants can grow to a height of 50 cm with adventitious and fibrous roots. Stems: flattened disc with tubular leaves that form a pseudo stem where their sheaths overlap. Leaves: 3-8 leaves per plant that are either erect or oblique. Flowers: pink or white flowers cluster on its stalks. Bulb: made up of layers, each of which corresponds to a leaf, generally oval, but their shape can vary globose, ovoid or elongate and its size varies depending on the cultivar. The outer leaf base dries and becomes thin and variously colored, forming the protective coat, while the inner leaf bases thicken when the bulb develops.
(Messiaen & Rouamba., 2004, PROSEA, 2016, Plantvillage, (n.d)
Variation in onion
The extensive diversity present in A. cepa has resulted in many suggestions for subgroup classifications, leading to a certain level of confusion in its taxonomy. Currently, the commonly followed informal classification divides the species into two cultivar groups:
1. Allium cepa var. cepa. (Allium Cepa (Cepa Group). This is the common what is commonly referred to simply as onions. This features large, typically solitary bulbs. These plants reproduce through seeds or by using seed-grown bulbils (sets). The vast majority of A. cepa belong to this group and include yellow onions, red onions, white onions and green onions. White onions have a white flesh with a sharper and more pungent flavor than yellow onions. Green onions are onions harvested while their shoots are still young and sold with the shoots attached. They have a mild flavor hence often used as a garnish. Scallions are green onions. Spring onions are also immature onions. They have a white, round bulb with long stems, and are also sold in bunches.
Ⓒ Maundu, 2005
Ⓒ Maundu, 2005
Ⓒ Maundu, 2005
Ⓒ Maundu, 2005
Ⓒ Maundu, 2005
Ⓒ Maundu, 2005
Ⓒ Maundu, 2005
2. Allium cepa var. aggregatum( Allium cepa (Aggregatum Group) are the Shallots. In this group, bulbs are smaller and cluster together, forming several to many aggregated bulbs. The group includes shallots, which produce a cluster of mainly small pointed bulbs (similar to garlic) and potato onions. Reproduction occurs vegetatively through lateral bulbs (daughter bulbs). Shallots have a rather mild garlic flavor. Their skin is pale brown to copper. Leaves are tubular and long.
Ⓒ Maundu, 2005
3. Chives (Allium schoenoprasum)
Chives should not be confused with green onions. They are smaller, thinner, and more delicate than green onions, Compared to green onions, chives have a much milder onion flavor. The bulbs are slender and grow in dense clusters from the roots. The stems are long and thin, hollow and tubular with a soft texture.
© Maundu, 2005
Common varieties grown in Kenya (short day or day neutral varieties)
• 'Red Creole'. This is a popular standard variety in high demand because of its good keeping quality. It produces mainly single onions from transplants, red, flat-round and with a pungent taste.
• 'Red Tropicana': Red bulbing type
• 'Red Tropicana F1 Hybrid'. Produces large, red, thick flat onions with firm pungent flesh. It is highly productive and therefore demands high levels of management. It keeps well in dry aerated store.
• 'Bombay Red'. It is a variety for dry and warmer conditions. It is small to medium sized, globe shaped, purplish red and pungent.
• 'Yellow Granex FI Hybrid'. This is an early maturing high yielding attractive, thick flat onion with thin yellow scales. The flesh is medium firm, crisp and mild in flavor. The shape and size is uniform leading to higher market prices, and the storage quality is good.
• 'Texas early Grano'. This is a fresh market, early maturing variety (100 - 120 days) with a rather short shelf life. It is yellowish, mild and not very pungent. The bulbs are high top shaped with dry yellow scales. It is a heavy yielder for high altitude regions. Ideal for fish salads.
• 'White Creole'. This is a white variety normally used for dehydration.
• 'Green bunching': Non-bulbing spring onion. It has attractive tasty dark green leaves. It is an early and highly productive onion grown for stems rather bulbs. It is tolerant to sun scotch and it is recommended for salads and fresh market.
When buying seed and not recognizing the variety name as one of the above, ask if it has been grown in Africa before. If not, better stick to a known variety in order not to lose the whole production.
(Plantvillage (n.d).
Onion varieties in East Africa.
In Tanzania, the favored onion type is Red Bombay. Its peak production occurs in March, May, and December and mainly originates from Mang’ola.
Additional well-liked varieties cultivated in the East Africa area encompass Red Pinoy F1, Red Creole, Bombay Red, and Texas Early Grano.
(Plantvillage (n.d)
Ecological information
In temperate zones onion is cool-season biennial, and is tolerant to frost. They produce bulbs with growing day lengths. Optimum temperatures for plant development are between 13 and 24degC, although the range for seedling growth is narrow, between 20 and 25degC. High temperatures favour bulbing and curing. In the tropics only short day or day neutral onion varieties will form bulbs. These thrive in warm to hot climates of 15-30degC. If the temperature greatly exceeds that required for bulbing, maturity is hastened and bulbs do not grow to maximum size, consequently lowering the yields.
Onions can be grown on any fertile, well-drained, non-crusting soil. The optimum pH range is 6.0 to 6.8, although alkaline soils are also suitable. Onions do not grow well in soils below pH 6.0. On light sandy soils irrigation is necessary. Irrigation could be either overhead or on drip. Onions at the bulbing stage need a substantial amount of water, but excessive moisture must be avoided during the growing season. Avoid application of fresh manure to the crop, as this will cause the plants to develop thick necks and too much leaf at the expense of bulb formation.
Agronomic aspects
Prior to planting, soils should be ploughed and disked sufficiently to eliminate debris and soil clods. In most commercial areas, beds 0.9 to 1.0 m wide are common, and 2 to 6 rows are seeded or planted on the bed. If two rows, they may be two-line (twin) rows with plants staggered to achieve proper spacing and high population density.
Proper seed selection is recommended to minimise problems of splits and doubles. Over-fertilization, uneven watering, and temperature fluctuations also influence bulb formation. Onion is propagated by seed (most common in the tropics) or sets (immature bulbs ripened during the previous season - in temperate zones).
|
|
|
Onion in nursery |
|
© A.A.Seif, icipe |
In the tropics the seed is usually sown in a nursery under a mulch cover. In the nursery prepare raised beds maximum 1 m wide and incorporate plenty of well-decomposed compost as well as additional rock phosphate. Make rows about 15 cm apart, sow the seeds and cover lightly with soil and mulch. Irrigate liberally for the first 10 days. Seed rate is 2-3 kg per ha. After the seed emerges, the mulch is removed. About 6-8 weeks after sowing, when the seedling has a base as thick as a pencil and is approximately 15 cm tall, the seedlings are transplanted to the field. ‘The ultimate yield of onion is determined by the number of leaves that are formed prior to bulbing.
Planting systems
• Nursery seeding and transplanting is the most common and practical option in the tropics. Transplants normally have 3 to 5 well-formed leaves at transplant time. Roots are pruned during planting, in order not to be bent upwards when transferred to the field. This facilitates early establishment of the plant.
• Any germinated bulb of above mentioned varieties would produce 3-6 good size bulbs in about 3 months when planted with the rains. Choose only healthy bulbs for propagation.
• Sets are used in some areas in the temperate zones to ensure large bulb size and uniform maturity. Sets are small dry bulbs, approximately 12 mm in diameter, which have been produced the previous season by seeding thickly or growing under conditions that favour rapid bulbing.
• Direct seedling is possible and gives excellent results where herbicides can be used and the season is sufficiently long to provide early pre-bulbing growth. In the tropics this method is impractical due to enormous weeding costs in an organic system.
Husbandry
Do not plant onions after the field has been planted with other Allium plants (e.g. garlic). Mulching onions with composted leaves and straw is highly recommended to maintain soil organic content, prevent soil-borne diseases, and suppress weeds. Planting onions in raised beds improves drainage and prevents damping-off diseases.
Weeding and harvesting are mostly done by hand, although chemical weed control is possible but not organic. Crop rotation is important to avoid the build-up of pests and diseases such as nematodes, Sclerotium and Fusarium.
© Maundu, 2016
Nutrient management
Onions respond very well to well decomposed organic manure. Organic manure at 25 to 40t/ha is recommended to obtain high bulb yield.
Harvest, post-harvest practices and markets
Harvest
Harvesting takes place 90-150 days after sowing. Onions are ready for harvest when the leaves collapse. Alternatively, the leaves can be bent over and left to dry for 10-12 days. The crop is pulled out by hand and kept for some days in the field with the bulbs covered by the leaves (= windrowing). The leaves are then cut off and the mature bulbs are bagged or packed in crates if they are to be stored. Unlike crops like Irish potatoes, onion bulbs don't effectively recover from cuts and surface wounds, underscoring the need to reduce mechanical damage during harvesting and handling prior to storage.
(Plantvillage, (n.d)
Post-harvest practices
Postharvest treatment of onion bulbs involves curing, storage, and managing dormancy to extend shelf life and prevent sprouting. Curing after harvest aids wound healing, improves handling qualities, limits the entry of organisms through injured tissues and promotes desirable skin appearance.
Onions are field-cured if weather allows, typically for a few days, until necks close, outer scales turn papery, and wounds heal. Alternatively, they can be indoor-cured at room temperature, either air-dried in windrows or placed in well-ventilated containers. Another method involves using warm (30°C), dry air circulated through onion piles in bins on slatted floors for 12-24 hours. Curing might result in up to 5% weight loss from the original harvest.
Green onions are best stored at 0°C and 95% relative humidity (RH), lasting up to 3 weeks. Best after curing to seal damage. Decay, sprouting, and rooting minimized at 0°C and 65-70% RH or 25-35°C. Storage causes moisture loss, shrinkage, and decreased diameter. Freshly harvested onions are dormant and will not sprout for a variable period of time (this depends on the variety). Storage will extend the dormant period. Sprouting will increase in storage temperatures above 4.4degC. It will decrease again as temperatures exceed 25degC.
(Messiaen & Rouamba., 2004, PROSEA, 2016, Plantvillage, (n.d)
Markets
According to FAO statistics in 2018 the top producers of onions were China (23,907509 tons) and India (19,415,425t), followed by Egypt and USA (about 3,000,000 t), Iran, Turkey, Russian Federation, Pakistan, Bangladesh and Brazil (from 2,345,768 to 1,657,441 t). Onions produced in European countries accounted for 10.9% of the world production, being Asia (65.5%) the most important producer.
In Africa, Onions are traditionally sold loose in bulk containers or in mesh bags of various weights. Several marketing alternatives are available to the onion grower: wholesale markets, cooperatives, local retailers, and roadside stands, farmer’s markets, community-supported agriculture.
Ⓒ Adeka et al., 2005
© Maundu, 2006
Fresh Quality Specifications for the Market in Kenya
The following specifications constitute raw material purchasing requirements
|
|
|
|
(c) S. Kahumbu, Kenya |
|
Nutritional value and recipes
Beyond their culinary versatility, onions boasts a commendable nutritional profile with a range of health benefits. Onions are notably low in calories, making them a weight-conscious choice. They provide a good source of dietary fiber, which aids in digestive health by promoting regular bowel movements and supporting gut flora. The sulfur compounds in onions, responsible for their pungent aroma, have been linked to potential heart health benefits. These compounds have been associated with reduced blood pressure, lowering cholesterol levels, and improving overall cardiovascular health.
Moreover, onions contain antioxidants such as quercetin, which has anti-inflammatory properties. These antioxidants help to combat oxidative stress, which can lead to chronic diseases and cellular damage. Regular consumption of onions has been correlated with a reduced risk of certain cancers, particularly those affecting the digestive tract.
Onions also contribute to bone health due to their content of calcium and vitamin C. Calcium is essential for maintaining strong bones and teeth, while vitamin C supports collagen synthesis, necessary for bone structure. Additionally, vitamin C aids the immune system, promoting the body's defense against illnesses and infections.
Furthermore, onions contain B vitamins, particularly folate and pyridoxine (vitamin B6), which are essential for energy metabolism, nerve function, and red blood cell production. Folate is especially important for pregnant women, as it aids in fetal development and helps prevent birth defects.
(Healthline (n.d), PubMed Central)
Further reading:
• https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24915405/
• https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/scallion-vs-green-onion#uses
Table 1: Proximate nutritional value per 100 g edible portion.
Code Food Name |
Onion, mature, red skinned, peeled, |
Onion, spring, raw |
Recommended daily allowance (approx.) for adults a |
Edible conversion factor |
1 |
0.78 |
|
Energy (kJ) |
177 |
130 |
9623 |
Energy (kcal) |
42 |
31 |
2300 |
Water (g) |
87.9 |
90.8 |
2000-3000c |
Protein (g) |
1.5 |
1.8 |
50 |
Fat (g) |
0.1 |
0.3 |
<30 (male), <20 (female)b |
Carbohydrate available (g) |
7.6 |
4.1 |
225 -325g |
Fibre (g) |
2.3 |
2.3 |
30d |
Ash (g) |
0.6 |
0.7 |
|
Minerals |
|||
Ca (mg) |
26 |
44 |
800 |
Fe (mg) |
0.9 |
1.3 |
14 |
Mg (mg) |
19 |
14 |
300 |
P (mg) |
40 |
34 |
800 |
K (mg) |
152 |
225 |
4,700f |
Na (mg) |
5 |
12 |
<2300e |
Zn (mg) |
0.16 |
0.3 |
15 |
Se (mcg) |
1 |
1 |
30 |
Bioctive compounds. |
|||
Vit A RAE (mcg) |
1 |
53 |
800 |
Vit A RE (mcg) |
2 |
105 |
800 |
Retinol (mcg) |
0 |
0 |
1000 |
b-carotene equivalent (mcg) |
10 |
632 |
600 – 1500g |
Thiamin (mg) |
0.02 |
0.04 |
1.4 |
Riboflavin (mg) |
0.04 |
0.06 |
1.6 |
Niacin (mg) |
0.3 |
0.6 |
18 |
Dietary Folate Eq. (mcg) |
14 |
48 |
400f |
Food folate (mcg) |
14 |
48 |
400f |
Vit B12 (mg) |
0 |
0 |
3 |
Vit C (mg) |
7 |
26 |
60 |
Source (Nutrient data): FAO/Government of Kenya. 2018. Kenya Food Composition Tables. Nairobi, 254 pp. http://www.fao.org/3/I9120EN/i9120en.pdf
RE=retinol equivalents.
RAE =Retinol activity equivalents. A RAE is defined as 1μg all-trans-retinol, 12μg beta-carotene, or 24μg α-carotene or β-cryptoxanthin.
*The specific species of nightshade is unknown.
$ Draining the water several times leaches away water soluble nutrients significantly.
a Lewis, J. 2019. Codex nutrient reference values. Rome. FAO and WHO
b NHS (refers to saturated fat)
c https://www.hsph.harvard.edu/nutritionsource/water/
d British Heart Foundation
e FDA
f NIH
g Mayo Clinic
Nutritive Value per 100 g of edible Portion
| Raw or Cooked Onion | Food Energy (Calories / %Daily Value*) |
Carbohydrates (g / %DV) |
Fat (g / %DV) |
Protein (g / %DV) |
Calcium (g / %DV) |
Phosphorus (mg / %DV) |
Iron (mg / %DV) |
Potassium (mg / %DV) |
Vitamin A (I.U) |
Vitamin C (I.U) |
Vitamin B 6 (I.U) |
Vitamin B 12 (I.U) |
Thiamine (mg / %DV) |
Riboflavin (mg / %DV) |
Ash (g / %DV) |
| Onion raw | 40.0 / 2% | 9.3 / 3% | 0.1 / 0% | 1.1 / 2% | 23.0 / 2% | 29.0 / 3% | 0.2 / 1% | 146 / 4% | 2.0 IU / 0% | 7.4 / 12% | 0.1 / 6% | 0.0 / 0% | 0.0 / 3% | 0.0 / 2% | 0.4 |
| Yellow Onions sauteed | 132.0 / 7% | 7.9 / 3% | 10.8 / 17% | 0.9 / 2% | 20.0 / 2% | 33.0 / 3% | 0.3 / 1% | 133.0 / 4% | - | 1.8 / 3% | 0.2 / 10% | - | 0.0 / 3% | 0.0 / 2% | 0.4 |
| Young Onions, Tops only | 25.0 / 1% | 5.6 / 2% | 0.1 / 0% | 1.8 / 4% | 61.0 / 6% | 33.0 / 3% | 1.9 / 11% | 260 / 7% | 4000 IU / 80% | 45.6 / 76% | 0.1 / 3% | 0.0 / 0% | 0.1 / 5% | 0.1 / 8% | 0.7 |
*Percent Daily Values (DV) are based on a 2000 calorie diet. Your daily values may be higher or lower, depending on your calorie needs.
Recipe
Onions and related species and varieties are used a lot in modern cooking. Traditional method of boiling has been replaced with frying with oil, onions, tomatoes, and adding seasonings. Each group has its distinct flavour and also different culinary use.
In East Africa, the onion is commonly eaten fresh in a type of salad called Kachumbari.
© Maundu, 2006
| The onion thrips are major pests of onions throughout Africa. The onion thrips attack an extensive range of crops, including cereals and broadleaved crops. They are tiny (1 mm in length), slender and very mobile insects. Adult thrips are pale yellow to brown in colour. Immature thrips are whitish to pale yellow. Both immature and adult thrips pierce the upper surface of the leaves and feed on the plant sap, generally on the developing leaves, deep inside the plant. This results in white and silvery patches on the leaves. The excreta of the thrips are clearly visible as small black dots on the silvery leaves. Severe infestations can cause browning of the leaf tips, slowing of plant growth, distortion of leaves and bulbs, and reduction in bulb size. Although thrips feeding during the early bulbing stage is the most damaging to yields, thrips must be controlled before onions reach this stage so that populations do not exceed levels that can be adequately controlled. Onions can tolerate higher thrips populations closer to harvest.
What to do:
For more information on neem click here.
For information on garlic bulb extract clik here
|
| The larvae of the onion fly, also called onion maggot is a major pest of onions. The maggot is small (about 8 mm in size when fully grown), white-cream coloured. It eats the lateral roots, then tunnels into the taproot and sometimes bores into the base of the stem. Attacked leaves wilt and the leaves turn bluish. The plants become shrivelled or eventually die. The maggots feed just above the base of seedlings killing them. A maggot can attack several seedlings in succession. This causes poor plant establishment resulting in many gaps in the field. The maggots are also found inside developing onion bulbs. Their feeding exposes the plant to infection by diseases such as bacterial soft rot. Pupae are light to dark-brown in colour, and about 7 mm in length. Pupae are found in the soil near the base of the plant. The adult is a brownish grey fly, somewhat smaller than house flies. When at rest, they keep their wings folded one over the other. Adult flies do not cause damage. They lay eggs in the soil surface near the germinating plants. Onion maggots are adapted to cool, wet weather, so usually they are less of a problem during hot dry periods. They prefer soils heavy in organic matter. The onion maggot attacks plants related to onion such as leeks, shallots and garlic.
What to do:
|
| Leafminers may cause damage to green onions. Damage is largely cosmetic, and mining on leaves may cause rejection of marketed onions, but generally does not affect plant growth. Damage in dry onions and garlic is of little concern unless populations become high to prematurely kill foliage. What to do:
|
| Purple blotch (Alternaria porri) Purple blotch attacks onion, garlic, leek and other Allium crops. Initially, small white sunken spots develop on the leaves. These enlarge and under moist conditions, turn purple with a yellowish border and are often covered with a sooty deposit of spores. After 3-4 weeks the leaves turn yellow and collapse. Bulbs may also be attacked, mainly at the neck. This can be seen as a yellow to reddish watery rot. A good timing of sowing or transplanting can minimise purple blotch attack by A. porri, depending on the local environmental conditions. The fungus requires rain or persistent dew for reproduction. It can grow through a wide temperature range of 6 to 33.8 °C. Optimum temperature of fungal growth is 25 °C.
What to do:
|
| Downy mildew (Peronospora destructor) It attacks young plants, appearing as white specks, usually confined to the oldest leaves of young plants. A greyish white mould develops rapidly in cool damp weather and progresses down the sheath, and plants eventually fall over and dry up. Optimum temperatures for fungal growth are between 13 and 20 °C. Because of the temperature requirements of the fungus, the disease is more serious in higher cooler areas. The fungus survives in seeds, bulbs, sets, and on plant debris. Spores are carried long distances by air currents. The fungus can infect onion, Welsh onion, Egyptian onion, garlic, shallot, leek and possibly some other species of Allium.
What to do:
|
| Bacterial soft rots (Erwinia carotovora subsp. carotovora) This is a big cause of loss in storage onions. Bacteria Erwinia carotovora subsp. carotovora) can enter the neck tissue as plants mature and then invade one or more scales. At this stage, the affected tissues are water-soaked and pale yellow to light brown. As the rot progresses, the invaded fleshy scales become soft. Diseased bulbs can be diagnosed by pressing on the bulb: a watery, foul-smelling fluid often can be squeezed from the neck of diseased bulbs. Bacterial soft rot bacteria enter only through wounds. Onion maggots (Delia antiqua) may carry the bacteria and introduce them while feeding. Onions with mechanical injuries, bruises or sunscald under warm, humid conditions are particularly susceptible to bacterial soft rot. Soft rot can affect many vegetables including carrots, celery, potato and parsnip.
What to do:
|
| Slippery skin (Pseudomonas allicolai pv. allicola) There are no symptoms on the outer surface of bulbs during early stages of disease development. When the bulb is cut open lengthwise, one or more of the inner scales can be found water-soaked or appears as if it has been cooked. The rot does not progress crosswise in the bulb. After the decay has progressed, the tissue begins to dry, the onion shrivels and secondary organisms can enter and cause a wet rot. The base of the bulb can be pressed hard enough to cause the centre core to slip out at the top, and for this reason the disease is known as slippery skin. The disease is favoured by high moisture.
What to do:
|
| Sour skin (Pseudomonas cepacia) In contrast to soft rot and slippery skin, infected scales are not water-soaked but are slimy and yellow. Symptoms usually visible only after onions are dug. The upper portion of the bulb shrinks, and in advanced stages of the disease, the outer dry skin readily slips off during handling while the centre of the bulb still remains firm. Outer layer of scales often becomes darkened and almost orange. Decay of inner scales leads to a soft rot that has a sour, vinegar-like odour. The disease is favoured by wet warm conditions.
What to do:
|
| Anthracnose (Onion smudge) (Colletotrichum circinans) It usually appears in fields just before harvest and continues to develop during storage period. Under warm and wet soil conditions, it can cause seedling damping-off. The most common symptom is the small dark green or black stains (dots) on outer scales of bulbs. The dots develop concentric rings. In severe cases, the fungus attacks the living tissue causing a collapse of fleshy scales. On coloured onions, the fungus is restricted to the neck of the bulbs making the flattened leaves colourless. The fungus survives on onions, sets and in the soil. Warm moist conditions favour development of the disease. Optimum temperature for infection is from 23.9 to 29.4 °C. White onions are very susceptible to the disease. Reduced market value results from marred bulb appearance and bulb shrinkage. It also attacks leeks and shallots.
What to do:
|
| White bulb rot (Sclerotium cepivorum) The disease occurs mainly in the field and seldom causes injury in storage. The disease is called white rot because of characteristic basal bulb rot where the tissue is covered with white mat of fungal growth. Later numerous rounded black fungal bodies (sclerotia), each about the size of a pin's head, develop. The leaves of diseased plants decay at the base, turn yellow, wilt, fall over and die. The older leaves are the first to die. The roots of affected plants are usually rotted making the plants easy to pull. Optimum temperature range for infection is from 15 to 18.3° C. The fungus survives in the soil as sclerotia and also in diseased onion sets and wild onion. It is most severe in light cool moist soils. Its host range includes Welsh onion, garlic, leek, shallot and some species of wild onion.
What to do:
|
| Affected leaves show small reddish to dusty orange spots (pustules). These later turn black and are covered until maturity by leaf epidermis. Leaves that are heavily infected turn yellow and die prematurely. A new crop of leaves may develop and the bulb size is usually reduced. The fungus attacks also leek, shallot and some wild species of Allium. The disease is favoured by high humidity coupled with moderate to low temperatures. Also excessive nitrogen in the soil favours disease development.
What to do:
|
| Fusarium basal rot (Fusarium oxysporium f.sp. cepae) The above ground symptoms constitute yellowing of leaf blades at the tip. The yellowing at later stages covers the whole blade. The affected leaves shrivel and decay. Diseased plants can be easily pulled out because the root system is rotted. Affected roots are dark brown, flattened, hollow and transparent. When diseased bulbs are cut vertically, a brown discolouration is evident. The fungus survives in any soil moisture that permits crop growth. Infection is facilitated by injuries to root system, Losses can occur in the field and in storage. The disease is most prevalent where onions are grown under high temperature conditions. Although of no economic importance the disease could attack garlic, shallots, chives and leeks. It also can survive in weed, Oxalis corniculata.
What to do:
|
References and Information links
References
- African museums. Allium cepa L. https://www.africamuseum.be/en/research/collections_libraries/biology/prelude/view_plant?pi=00840&cat=&cur_page=7
- AIC, Ministry of Agriculture and Livestock (2003). Fruits and Vegetables Technical handbook.
- Allium cepa L. in GBIF Secretariat (2021). GBIF Backbone Taxonomy. Checklist dataset https://doi.org/10.15468/39omei accessed via GBIF.org on 2021-12-21.
- Beije, C.M., Kanyagia, S.T., Muriuki, S.J.N., Otieno, E.A., Seif, A.A., Whittle, A.M. (1984). Horticultural Crops Protection Handbook. KEN/75/028 and KEN/80/017. National Horticultural Research Station, Thika, Kenya.
- Bohlen, E. (1973). Crop pests in Tanzania and their control. Federal Agency for Economic Cooperation (BFE), Germany. ISBN: 3-498-64826-9.
- CAB International (2005). Crop Protection Compendium, 2005 Edition. Wallingford, UK . www.cabi.org
- East African Seed Co. Ltd. Africa's Best Grower's Guide www.easeed.com
- Foster, R., Flood, B. (Eds) (1995). Vegetable Insect Management with emphasis on the Midwest. Purdue Research Foundation. ISBN: 0-931682-52-5.
- How to Manage Pests. Onion and Garlic. UC Pest Management Guidelines. UC IPM Online. Statewide Integrated Pest Management Program. University of California. Agriculture and Natural Resources. www.ipm.ucdavis.edu
- Kuepper, G. (2004). Thrips Management Alternatives in the Field. National Sustainable Agriculture Information Service- ATTRA. attra.ncat.org
- Ministry of Agriculture and Rural development and Japan International Cooperation Agency (2000). Local and Export Vegetables growing Manual. Agricultural Information Resource Centre, Nairobi, Kenya
- Nutrition Data.www.nutritiondata.com.
- Oisat: Organisation for Non-Chemical Pest Management in the Tropics. www.oisat.org
- Schmutterer, H. (1995). Effects on Viruses and Organisms. Thysanoptera: Thrips. In: The neem tree Azadirachta indica A. Juss. and other meliaceous plants sources of unique natural products for integrated pest management, industry and other purposes. (1995). Edited by H. Schmutterer in collaboration with K. R. S. Ascher, M. B. Isman, M. Jacobson, C. M. Ketkar, W. Kraus, H. Rembolt, and R.C. Saxena. Pages VCH. Pages 251-254. ISBN: 3-527-30054-6.
- Shanmugasundaram, S. (2001). Suggested cultural practices for onion. Edited by T. Kalb. AVRDC Training guide, AVRDC.
- Sherf, A.F., Macnab, A.A. (1986). Vegetable Diseases and Their Control. 2nd. Edition. John Wiley & Sons Inc. ISBN: 0-471-05860-2.
- The World Vegetable Center Learning Center (Onion). www.avrdc.org
- Youdeowei, A. (2002). Integrated pest management practices for the production of vegetables. GTZ. Integrated Pest Management Extension Guide 4. Published by The Ministry of Food and Agriculture (MOFA) Plant Protection and Regulatory Services Directorate (PPRSD), Ghana with the German Development Cooperation (GTZ). ISBN: 9988-0-1088-5.
Information links
https://www.atlasbig.com/en-in/countries-by-onion-production
Contact Information
- Corner Shop, Nairobi: cornershop@africaonline.co.ke, +254 (0) 0716 905 486, (20) 2712268/9
- Green Dreams: info@organic.co.ke +254 (0) 724 781 971/ 0722 562 717
- Horticultural Crops Directorate: info@agricultureauthority.go.ke, +254 20 2536869, 0722 200 556
- Kalimoni Greens: www.kalimonigreens.com , +254 (0) 708 278 273
- Karen Provision Stores, Nairobi: kps@nbi.ispkenya.com +254 20 882 252, 0736 371 437
- Muthaiga Green Grocers, Nairobi
- Nakumatt Supermarket: info@nakumatt.net, +254 (0) 733 632 130, 0722 204 931, (20) 3599991-4
- Horticulture Research Institute, Thika: director.hri@kalro.org. +254 (20) 2055038
- Uchumi Supermarket: info@uchumi.com +254 20 8020081 - 5, 0733 410 028,
- Zuchinni Green Grocers, Nairobi: +254 (20) 2215067
Review Process
Dr. Patrick Maundu, James Kioko, Charei Munene and Monique Hunziker, July 2024